Product Categories
Contact Us
Wen zhou boxin steel industry Co., Ltd
Add:4102 Yong Qiang Avenue,Longwan District, Wenzhou. China
Tel:+86-577-86927958
Pho:+8618058896089
Fax:+86-577-86927988
E-mail:info@boxinsteel.com
Steel Knowledge
Stainless steel heat exchanger: stainless steel is a kind of material, is one of the components of the heat exchanger, placed within the cylinder for the exchange of heat between the two media.

Stainless steel heat transfer tube has the following advantages:
1. The heat transfer tube adopts 0.5-0.8mm thin-walled pipe to improve the overall heat transfer performance. Under the same heat transfer area, the overall heat transfer coefficient is 2.121-8.408% higher than that of copper pipe.
2. As the material using SUS304 high-quality stainless steel alloy, it has a high hardness, the pipe's steel is also significantly improved, therefore, has a strong impact resistance and anti-vibration performance.
3. As the inner wall of the pipe is smooth, the thickness of the underlying laminar flow is thinned, which enhances the heat transfer and improves the anti-fouling performance. In order to eliminate the welding stress, in the protective gas to 1050 ℃ high temperature heat treatment. Steel pipe are used to check the pressure difference, air pressure test to 10MPa, 5 minutes without pressure drop.
Copper tube: also known as copper, non-ferrous metal tube, is a pressed and drawn seamless tube. Brass with strong, corrosion-resistant features, and become a modern contractor in all residential commercial housing water pipe, heating, cooling pipe installation of choice. Brass is the best water supply pipe.

Advantages of copper:
1, lighter weight, good thermal conductivity, low temperature strength. Commonly used in the manufacture of heat transfer equipment (such as condenser, etc.). Also used in oxygen equipment in the assembly of low temperature piping. Small diameter brass is often used to transport pressure of the liquid (such as lubrication systems, hydraulic systems, etc.) and used as instrument pressure tube.
2, brass with a strong, corrosion-resistant characteristics, and become a modern contractor in all residential commercial housing water pipe, heating, cooling pipe installation of choice.
3, copper tube into many advantages: it is strong, with the general high-strength metal; at the same time than the general metal easy to bend, easy to reverse, easy to crack, easy to break, and has a certain anti-frost and impact resistance, so The water supply system in the construction of the copper pipe once installed, safe and reliable to use, even without maintenance and maintenance.
Brass shortcomings: the copper tube, the high price is its biggest drawback, is the most high-end water pipes, usually after the installation of welding process will not leak water. The connection of copper pipe interface mainly depends on the construction level, the construction quality requirements are higher.
The following will be from the following aspects to explain the difference between copper and stainless steel heat transfer tube
Copper tube and stainless steel heat exchanger performance comparison is as follows:
First, the performance of copper and stainless steel heat transfer tube compared to the thermal conductivity
Since the thermal conductivity of brass is 100W / m ℃, the thermal conductivity of stainless steel tube is 13W / m ℃, which of course affects the overall heat transfer coefficient. However, the wall thickness of the stainless steel pipe can be reduced to 0.5 to 0.8 mm, and the copper tube due to strength and erosion wear and other original
Because its wall thickness can not be less than 1.2mm.
According to the formula: Rc = (1) where: Rc - thermal conductivity, m2k / w. Λ - thermal conductivity, W / (m.k).
Δ-wall thickness, m
Pipe is constant, λ unchanged, according to formula (1), δ smaller, Rc smaller, the greater the heat transfer coefficient. This can narrow the gap between the stainless steel pipe and the overall heat transfer coefficient of the brass.
As the brass inside and outside the wall is more rough than stainless steel, easy to scale, increasing the thermal resistance of the brass, which in turn makes the copper tube and the overall heat transfer coefficient of stainless steel narrow the gap.
Second, the performance of brass and stainless steel heat exchanger contrast convection heat release
The use of stainless steel tube or the use of brass, tube flow rate is turbulent. The greatest factor affecting convective heat dissipation is the thickness of the laminar underlayer because the heat transfer in the underlying layer is heat conduction and the thermal conductivity of the water is low. In the case of the same flow state, the thickness of the laminar bottom layer depends on the roughness of the inner wall of the tube. Copper tube on the surface of the oxide, the roughness is much larger than the stainless steel tube, brass base layer of the thickness of the lower than the thickness of the bottom layer of stainless steel. This makes the convection and exothermic coefficient of the stainless steel tube convection heat dissipation coefficient greater than the brass.
Rw = (2)
Where: Rw - convection heat release resistance, m2k / w. Αw-convective heat release coefficient, w / m2.k. According to the formula (2) the larger αw, the smaller the Rw.
Third, the performance of copper and stainless steel heat exchanger compared to the condensation heat release coefficient
Condensation and exothermic coefficients are membrane-like condensation and bead-like condensation. The emissivity coefficient of the beads is much larger than that of the membrane-like condensation. But the outer wall of the stainless steel tube and the outer wall of the brass pipe which is more clear is not clear, but it can be said that most of the outer wall of the two kinds of membrane-like condensation. The size of the exothermic coefficient of the membrane-like condensation is very large in relation to the thin thickness of the film because the heat transfer coefficient of the water film is particularly low and the thickness of the film depends on the roughness of the outer wall of the tube. Copper pipe wall due to the relationship between the oxide layer, much rough than the stainless steel tube. Therefore, the external heat dissipation coefficient of the outer wall of the stainless steel tube is larger than that of the outer wall of the copper pipe.
Rm = (3)
Where: Rm-tube outer wall of the condensation heat dissipation, m2k / wαm-tube outer wall of the condensation heat release coefficient, w / m2.k. According to the formula (3), the larger the αm, the smaller the Rm.
Fourth, the performance of copper and stainless steel heat transfer tube compared to the overall heat transfer coefficient
K = (4)
Where: R - total resistance, m2k / w. K - the overall heat transfer coefficient, w / m2.k.
From (4) we can see: convection thermal resistance, thermal resistance and condensation heat dissipation are reduced, the total thermal resistance decreases: the total thermal resistance decreases, the overall heat transfer coefficient increases.
In the case of the same wall thickness, the overall heat transfer coefficient of stainless steel pipe is 6% lower than that of brass. As a result of the use of thinner than the brass stainless steel pipe, stainless steel pipe, the overall heat transfer coefficient and condensation heat dissipation than copper, so that the overall heat transfer coefficient of stainless steel pipe is improved.
Copper and stainless steel heat transfer tube heat transfer performance comparison table
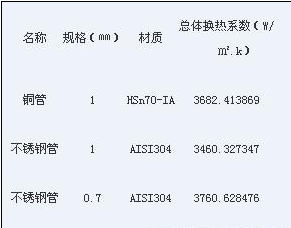
Fifth, the performance of copper and stainless steel heat transfer tube compared to the long-term economy
With the running time, copper oxide layer will become thicker and thicker, the heat transfer effect will be getting worse. While the stainless steel is basically not oxidized, or the oxidation rate is very slow. Therefore, the stainless steel pipe heat exchanger and copper heat exchanger if put into operation at the same time, the longer the running time, the economy of stainless steel pipe heat exchanger will be more and better than the copper heat exchanger. At the same time, the brass of the cooling water in the debris adsorption capacity is much stronger than the stainless steel pipe, greatly reducing the economy of the equipment.
Six, copper pipe and stainless steel heat exchanger performance comparison of the safety performance comparison
Brush and stainless steel heat transfer tube engineering characteristics table
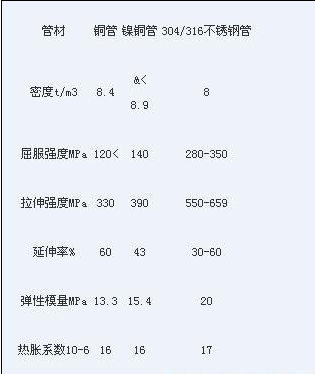
It can be seen from the above table: stainless steel tube yield strength and tensile strength than copper, stainless steel pipe life is bound to be longer than the copper, thermal expansion coefficient than copper, and tube plate closer, It is not easy due to thermal expansion and contraction of the surface damage to the tube or affect the mouth.
Corrosion resistance of copper and stainless steel heat transfer tubes
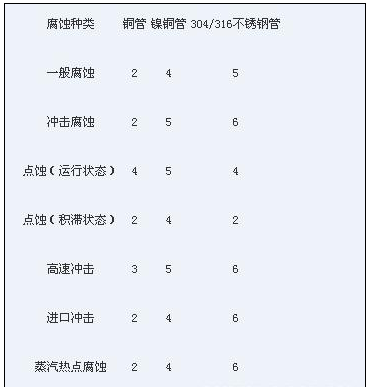
From the table we can see: stainless steel pipe and copper compared to the advantages of good resistance to erosion, can withstand the impact of steam in the high-speed impact corrosion; anti-ammonia corrosion performance: water-resistant impact corrosion, to achieve no copper ion system , And the PH value can be increased to reduce the corrosion rate, can improve the cooling water flow rate, up to 2.3m / s, up to 3.5m / s, which can improve the overall heat transfer coefficient, but also reduce the deposition of impurities in the tube.
Related News
- Spring steel standards...
- National standard of bearing steel...
- Seamless steel tube series...
- Welded pipe standard...
- How to choose a water supply network in the valve...
- 12cr1movG high-pressure alloy tubes what are the specific cl...
- Welded pipe standard...
- What is a pipe?...
- What is a coated steel pipe?...
- Specifications and appearance quality of boiler tubes...
 Blue
Blue  info@boxinsteel.com
info@boxinsteel.com